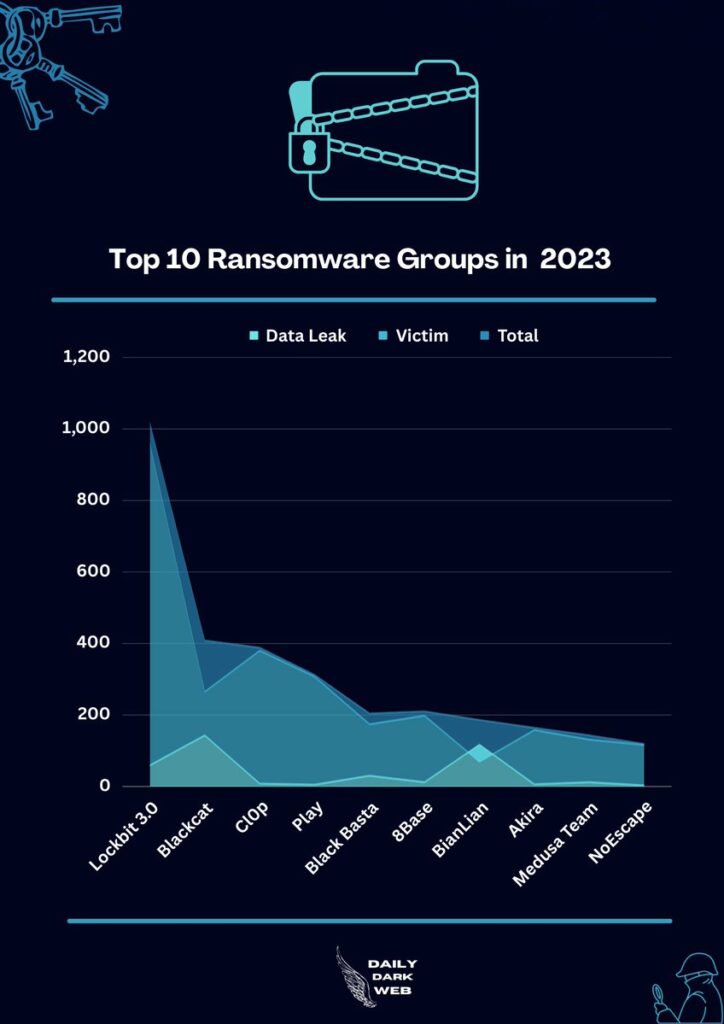
By employing a multitude of advanced techniques like double extortion along with other illicit tactics, ransomware groups are continually evolving at a rapid pace.
In a double extortion tactic, the threat actors not only encrypt data but also threaten their victims to release their sensitive information or data.
In recent times, it’s been noted by security researchers that they are increasingly targeting high-profile victims to maximize their profits by using the following things:-
- Sophisticated malware
- Demands larger ransom amounts
Besides this, some groups also collaborate or share their resources, through which they make things more challenging for law enforcement and other security experts to combat their activities effectively.
Table of Contents:
Types Of Ransomware
10 Notorious Ransomware Gangs of 2023
LockBit
Alphv/BlackCat
Clop
Royal
BlackByte
Black Basta
Ragnar Locker
Vice Society
Everest
BianLian
Types Of Ransomware
Here below, we have mentioned all the types of ransomware used by the threat actors for their illicit goals and purposes:-
- Locker Ransomware
- Crypto-Ransomware
- Scareware
- Leakware
- Ransomware As a Service (RaaS)
However, two types of ransomware are very popular and used widely by threat actors are:-
- Locker ransomware
- Crypto ransomware
Ransomware Gangs’ Motivations
Here below we have mentioned all the motivations:-
- Financial Gains
- Ease of Use
- Powerful Monetisation
- Evolving Technologies
- Politics
10 Notorious Ransomware Gangs of 2023
In this blog, we have covered the top 10 notorious ransomware gangs of 2023, and here below, we have mentioned them:-
- LockBit
- Alphv/BlackCat
- Clop
- Royal
- BlackByte
- Black Basta
- Ragnar Locker
- Vice Society
- Everest
- BianLian
Now, let’s discuss the above-mentioned top 10 notorious ransomware gangs of 2023:-
LockBit

LockBit, a notorious ransomware group, emerged in September 2019, employing a global ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) model.
They target global companies and released versions 2.0 and 3.0 in June 2021 and 2022, respectively, featuring:-
- BlackMatter-based encryptors
- New payment methods
- A bug bounty program
Despite their innovations, a setback occurred when the developer leaked LockBit Black’s builder online, compromising its legitimacy.
Alphv/BlackCat

BlackCat/AlphV, a suspected successor to dissolved ransomware groups, operates in Rust to avoid detection and successfully encrypt victims’ files, and this ransomware group targeted:-
- Western Digital
- Sun Pharmaceuticals
ALPHV/BlackCat is the first Rust-written ransomware, requiring a specific access token and featuring encrypted configurations, including:-
- Services/Processes lists
- Whitelisted directories/Files
- Stolen credentials
Apart from this, it erases Volume Shadow Copies, exploits privilege escalation, and alters file extensions to “uhwuvzu” using AES and RSA encryption.
Clop

The Clop ransomware emerged in 2019 and used a collaborative ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) model with sophisticated social engineering tactics. Since then, this stealthy group has managed to extort over $500 million from several companies globally.
The operators of this group target a wide range of entities by exploiting the following things:-
- Software vulnerabilities
- Phishing
One of their notable attacks is they hacked Accellion’s File Transfer Appliance in 2020, affecting global organizations.
Clop encrypts files with “.clop” extension, denying access and teasing data leaks as proof. The operators of Clop employ double extortion tactics, which is why they threaten their victims to expose or sell their sensitive data along with high cryptocurrency demands, which shows the sharp shift from typical ransomware trends.
Royal

Royal Ransomware emerged in 2022 as a sophisticated threat, ranking among the year’s most terrifying campaigns.
Operating under Dev-0569, they primarily targeted high-profile victims like the following we have mentioned to demand millions:-
- Silverstone Circuit
- A major US telecom
Unlike typical ransomware, Dev-0569, a private group, directly purchases network access and utilizes double extortion tactics, which distinguishes it from other cybercrime operations.
BlackByte

BlackByte surfaced in July 2021, drawing FBI and USS attention for targeting US critical infrastructure sectors.
Despite a Trustwave decrypter released in October 2021, BlackByte evolved with multiple keys and continued operations, possibly linked to Conti’s rebranding.
It persists in global attacks but steers clear of Russian entities like:-
- LockBit
- RansomEXX
Black Basta

Black Basta ransomware surfaced in February 2022 with a multitude of unique traits. It erases Volume Shadow Copies, replacing them with a:-
- JPG wallpaper
- ICO file
Unlike others, it encrypts files indiscriminately but spares critical folders, and using the ChaCha20 algorithm, it encrypts with a hard-coded RSA public key.
Besides this, the file size dictates full or partial encryption, with a .basta extension added.
Ragnar Locker

Since Dec 2019, the Ragnar Locker ransomware and its operators have targeted global infrastructure, hitting the following entities:-
- Portuguese carriers
- Israeli hospital
Operating on Windows by exploiting Remote Desktop Protocol, the group demanded huge payments using a double extortion strategy.
Not only that, but threat actors also threaten the victims with decryption tools and sensitive data release. While Ragnar Locker ransomware is considered one of the most dangerous, as it has a high threat level due to critical infrastructure attacks.
Vice Society

Vice Society is a Russian-speaking hacking group that emerged in 2021. This threat group specializes in ransomware attacks on the following sectors:-
- Healthcare
- Education
- Manufacturing
They operate independently, and they have hit Europe and the U.S. with a double extortion approach through which they demanded over $1 million during their initial ransom and settled it around $460,000.
It penetrates exploiting the internet-facing apps and compromised credentials. While besides this, using SystemBC, PowerShell Empire, and Cobalt Strike, they move laterally.
Even it also exploits the Windows services, PrintNightmare, and evades detection with disguised malware and process injection.
Everest

Everest has been active since Dec 2020, and it has transitioned from data exfiltration to ransomware and now focuses on Initial Access Broker services.
Its targets span industries, with a focus on the Americas, capital goods, health, and the public sector. This notorious group is known for hitting AT&T and South American government entities, and besides this, it’s been linked to the following ransomware:-
- EverBe 2.0
- BlackByte
It has been operating discreetly, and till now, it has managed to list nearly 100 organizations on its dark website. Uncommonly, the group acts as an Initial Access Broker, a shift from direct ransomware attacks, which is a rare move in the cybercriminal landscape.
BianLian

BianLian ransomware first emerged in June 2022 and is written in the Go language. However, it exfiltrates the data via:-
- RDP
- FTP
- Rclone
- Mega
Primarily it targets the following sectors:-
- Financial institutions
- Healthcare
- Manufacturing
- Education
- Entertainment
- Energy
Initially, they used encryption for ransom, but they later incorporated data exfiltration, threatening disclosure. However, Avast’s decryptor in January 2023 shifted its focus to data theft, terminating file encryption.
BianLian hacks via spearphishing, gaining entry through malicious emails or compromised links. Once in, the malware connects to its command server, downloads tools, and secures a lasting hold on the system.
Source: Cybersecuritynews.com